Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- Home
- General Surgery
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
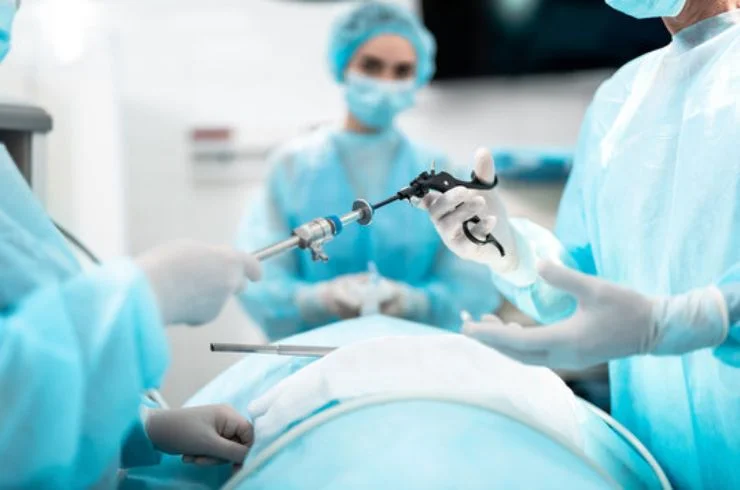
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the gallbladder, typically when it is affected by gallstones, inflammation, or infection. This procedure offers a faster recovery, minimal scarring, and a high success rate, making it the preferred treatment option for gallbladder diseases.
What is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
The gallbladder is a small organ located just beneath the liver, responsible for storing bile, which aids in digestion. However, when gallstones or other issues affect the gallbladder, it can lead to painful symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and severe abdominal pain. In some cases, the gallbladder may become inflamed or infected, requiring surgical intervention to remove it.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy involves the removal of the gallbladder through small incisions using a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera). The procedure is minimally invasive and is preferred over traditional open surgery due to its numerous benefits.
Why Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is recommended for patients who experience the following conditions:
- Gallstones: Solid particles that form in the gallbladder and block the bile ducts.
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by infection or gallstones.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas due to gallstones.
- Biliary Dyskinesia: Poor functioning of the gallbladder.
- Choledocholithiasis: Gallstones that have moved into the bile duct, causing blockages.
If these conditions are left untreated, they can lead to more serious complications, including infections and digestive issues. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is an effective solution to remove the gallbladder and prevent these problems.
The Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Procedure
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgery that involves several key steps:
- Preparation: The patient is given anesthesia to ensure they remain asleep and pain-free during the procedure.
- Small Incisions: A few small incisions (typically 3 to 4) are made in the abdomen.
- Laparoscope Insertion: A laparoscope, equipped with a light and camera, is inserted through one of the incisions to allow the surgeon to view the internal organs on a monitor.
- Gallbladder Removal: The surgeon carefully removes the gallbladder through one of the incisions using specialized instruments.
- Closure: The small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue, and the procedure is completed.
The surgery typically takes about 1 to 2 hours, and most patients can go home the same day or the day after.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- Minimally Invasive: The small incisions result in less trauma to the body, reducing the risk of complications.
- Faster Recovery: Patients usually experience less pain, quicker healing, and can return to normal activities within a few days.
- Minimal Scarring: The small incisions leave behind minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: In many cases, the procedure is done on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to go home on the same day.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Since the incisions are smaller and less invasive, the risk of infection is reduced.
